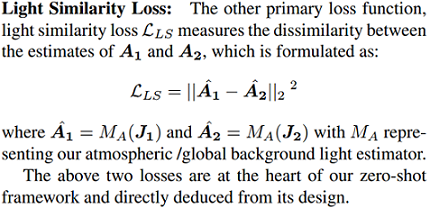Zero-shot Single Image Restoration through Controlled Perturbation of Koschmieder's Model
Aupendu Kar, Sobhan Kanti Dhara, Debashis Sen, Prabir Kumar Biswas
Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India
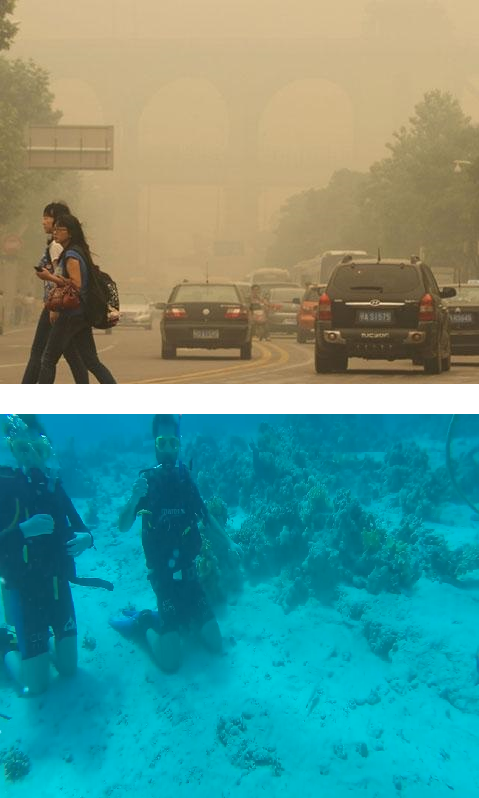
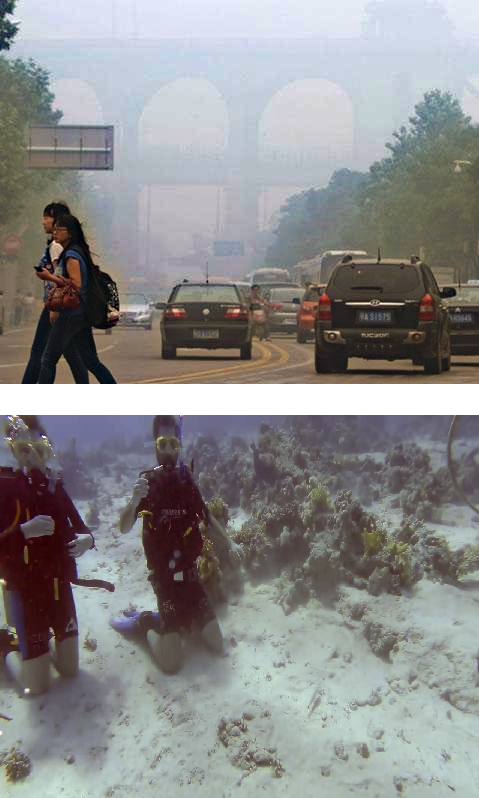
Use the slider to compare before and after






Abstract
Real-world image degradation due to light scattering can be described based on the Koschmieder's model. Training deep models to restore such degraded images is challenging as real-world paired data is scarcely available and synthetic paired data may suffer from domain-shift issues. In this paper, a zero-shot single real-world image restoration model is proposed leveraging a theoretically deduced property of degradation through the Koschmieder's model. Our zero-shot network estimates the parameters of the Koschmieder's model, which describes the degradation in the input image, to perform image restoration. We show that a suitable degradation of the input image amounts to a controlled perturbation of the Koschmieder’s model that describes the image's formation. The optimization of the zero-shot network is achieved by seeking to maintain the relation between its estimates of Koschmieder’s model parameters before and after the controlled perturbation, along with the use of a few no-reference losses. Image dehazing and underwater image restoration are carried out using the proposed zero-shot framework, which in general outperforms the state-of-the-art quantitatively and subjectively on multiple standard real-world image datasets. Additionally, the application of our zero-shot framework for low-light image enhancement is also demonstrated.
Highlights
- To the best of our knowledge, the proposed approach is the first that can be used for image restoration in all the application domains where the degradations can be formulated based on the Koschmieder's model.
- To the best of our knowledge, the proposed zero-shot learning approach for dehazing and underwater image restoration is first of a kind, where a prior based loss function or regularizer is not required. Further, our approach is probably the first zero-shot approach for underwater image restoration.
- Despite being a zero-shot approach, our approach outperforms or performs as good as the state-of-the-art in real-world image dehazing and underwater image restoration. We further demonstrate the use of our approach for low-light image enhancement, where the Koschmieder's model can be employed.
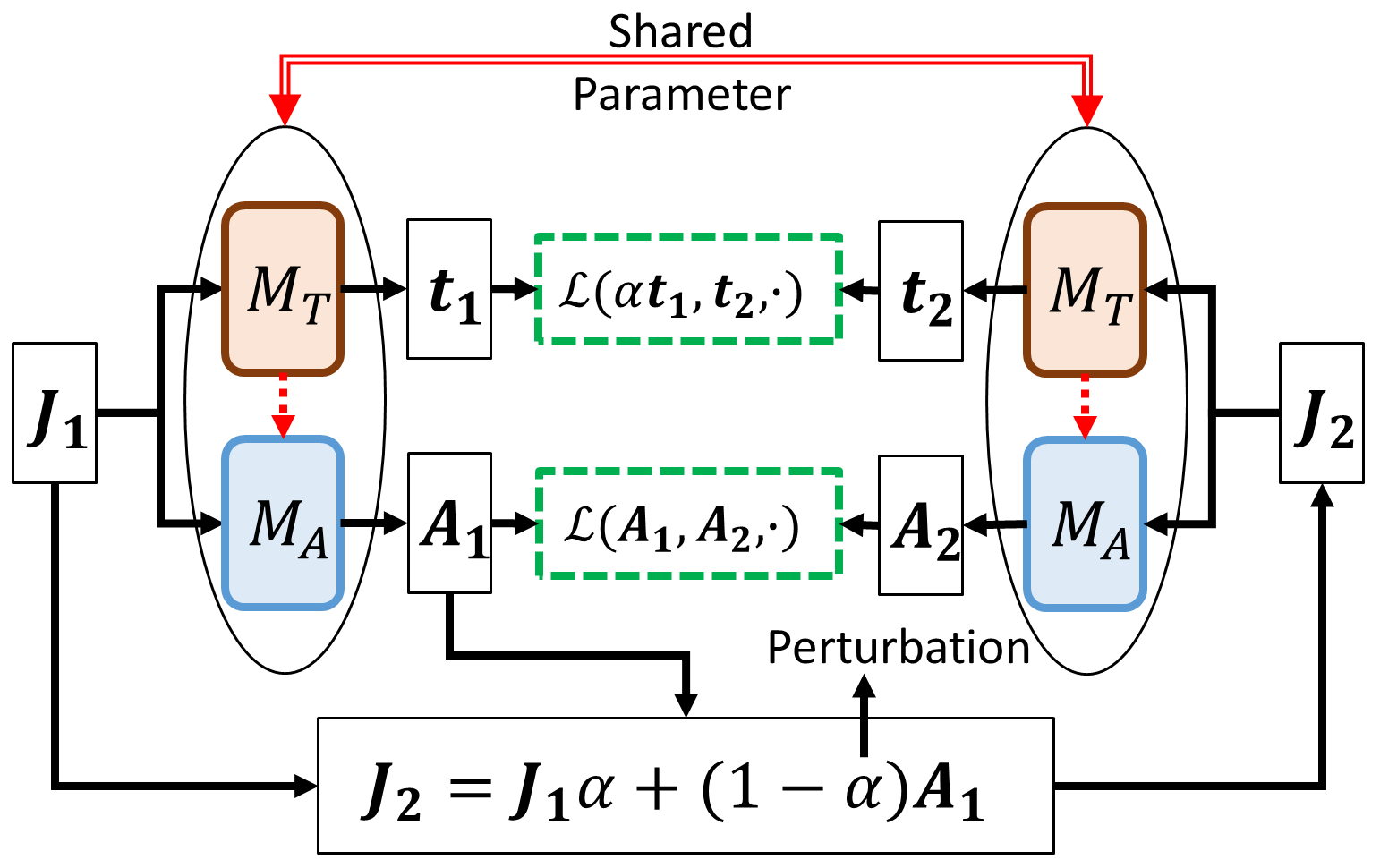
Zero-Shot Learning Framework
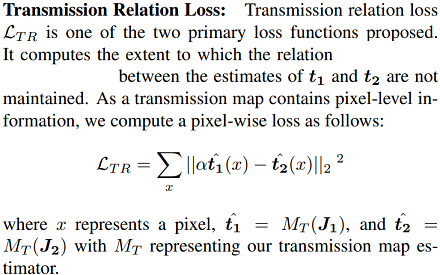
Loss Function
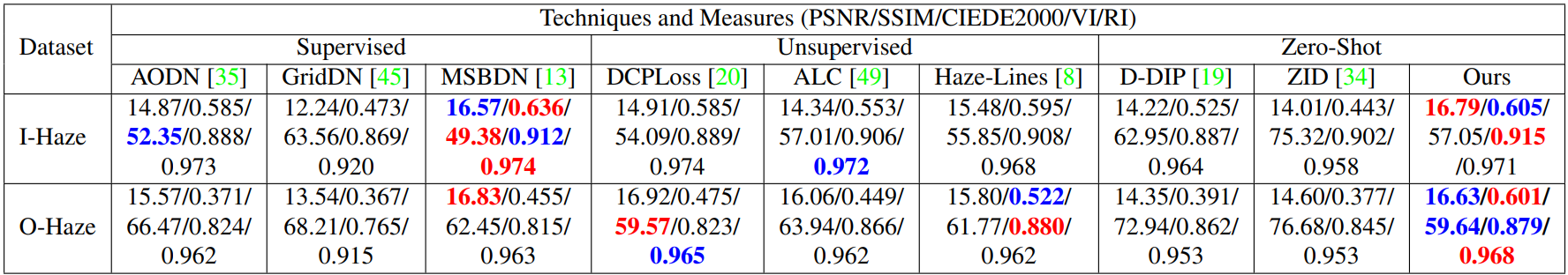
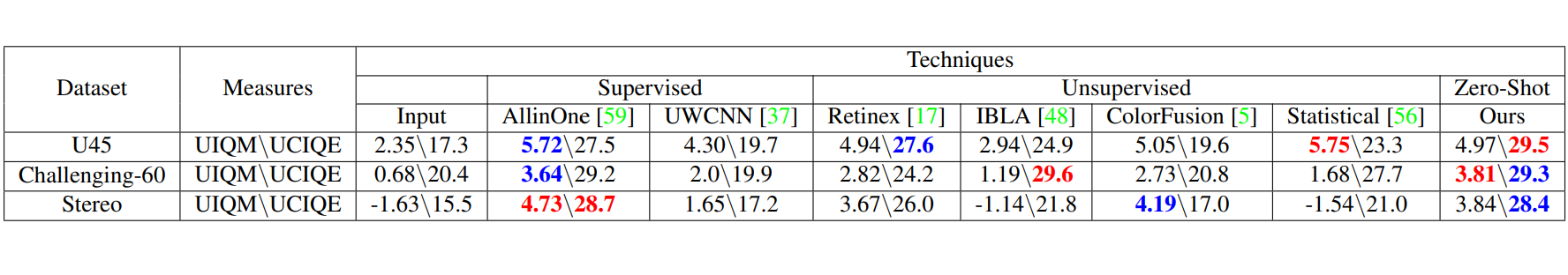
Results

Ablation Studies
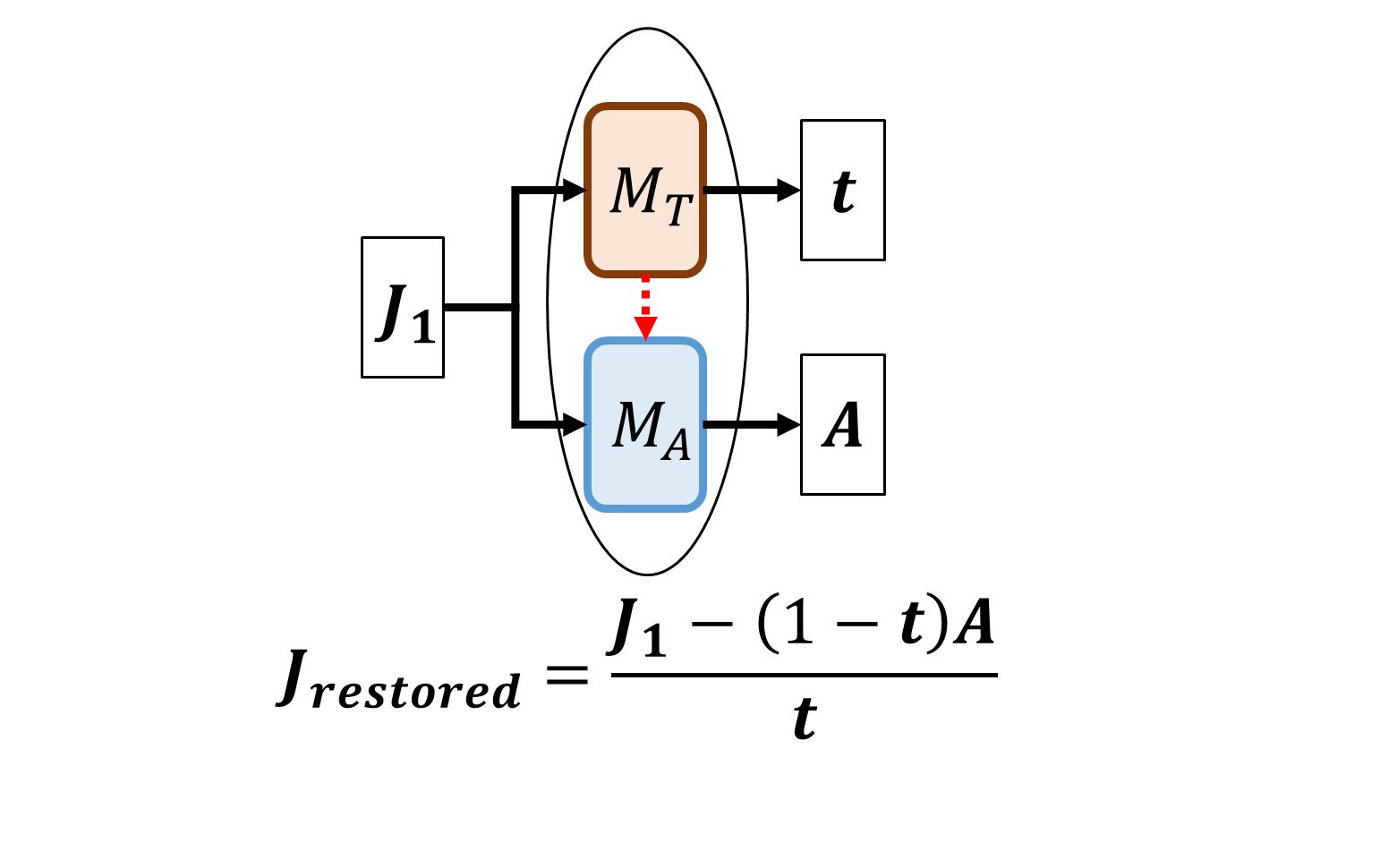
The Estimates in our Restoration Approach
Downloads
References
- Swinehart, D.F., 1962. The beer-lambert law. Journal of chemical education, 39(7), p.333.
- Gandelsman, Y., Shocher, A. and Irani, M., 2019. " Double-DIP": Unsupervised Image Decomposition via Coupled Deep-Image-Priors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 11026-11035).
- Li, B., Gou, Y., Liu, J.Z., Zhu, H., Zhou, J.T. and Peng, X., 2020. Zero-shot image dehazing. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 29, pp.8457-8466.
- Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Liu, X., Shen, Y., Zhang, S. and Zhao, S., 2019, October. Zero-shot restoration of back-lit images using deep internal learning. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (pp. 1623-1631).
- Uplavikar, P.M., Wu, Z. and Wang, Z., 2019, May. All-in-One Underwater Image Enhancement Using Domain-Adversarial Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (pp. 1-8).
Citation (BibTeX)
@InProceedings{Kar_2021_CVPR,
author = {Kar, Aupendu and Dhara, Sobhan Kanti and Sen,
Debashis and Biswas, Prabir Kumar},
title = {Zero-shot Single Image Restoration through Controlled
Perturbation of Koschmieder’s Model},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2021},
pages = {16205-16215}
}